Happy New Year to all! I decided to translate old Japanese version posts to English for studying English in this year. First of all, I try to translate following post.
ryuchan.hatenablog.com
I would like to summarize the tuning of SQL Server. First, let's look at how to extract queries that don't use indexes, SQL Server tuning makes heavy use of dynamic management views that start with "dm_*". At this time, mainly use the following three tables to find queries that don't use indexes.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_statsGet information about the missing index group.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_groupsTable required to JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats and sys.dm_db_missing_index_details.
- sys.dm_db_missing_index_detailsGet detailed information about the missing indexes.
You can use the following query to find the missing index. (Using the usual AdventureWorksDB.)
USE AdventureWorks2012 SELECT gs.last_user_seek AS [Time of last seek], id.statement AS [Table name] , id.equality_columns AS [Columns that can be used for equality predicates], id.inequality_columns AS [Columns that can be used for inequality predicates] , id.included_columns AS [Columns required as included columns], gs.unique_compiles AS [Number of compilations and recompilations], gs.user_seeks AS [Number of seeks generated by the query.] FROM sys.dm_db_missing_index_group_stats AS gs INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_groups AS ig ON gs.group_handle = ig.index_group_handle INNER JOIN sys.dm_db_missing_index_details AS id ON ig.index_handle = id.index_handle WHERE id.[database_id] =DB_ID() Order By gs.last_user_seek ASC
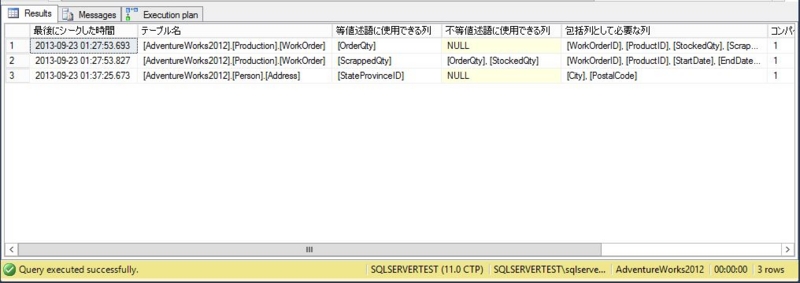
After executing some queries without indexes, the above query will look like the below. I explain how to improve the area in the red frame.

- Last seek time2013-09-23 03:42:41.773
- Table name[AdventureWorks2012]. [Purchasing]. [PurchaseOrderHeader].
- Columns that can be used for equality predicates [RevisionNumber].
- Columns that can be used for inequality predicatesNULL
- Columns required as inclusive columns[PurchaseOrderID], [Status], [EmployeeID], [VendorID], [ShipMethodID], [OrderDate], [ShipDate], [SubTotal], [TaxAmt], [Freight], [TotalDue], [ModifiedDate].
- Number of compilations and recompilations1
- Number of seeks generated by the query2
From the above results, it can be determined that the RevisionNumber column, which has no index is specified in the WHERE clause. In addition, you can see that the following included columns are required.
[PurchaseOrderID], [Status], [EmployeeID], [VendorID], [ShipMethodID], [OrderDate], [ShipDate], [SubTotal], [TaxAmt], [Freight], [ TotalDue], [ModifiedDate]
Therefore, you can solve this problem by executing the following query.
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX IX_PurchaseOrderHeader_RevisionNumber ON [Purchasing].[PurchaseOrderHeader] ([RevisionNumber]) INCLUDE ([PurchaseOrderID],[Status],[EmployeeID],[VendorID],[ShipMethodID],[OrderDate],[ShipDate],[SubTotal],[TaxAmt],[Freight],[TotalDue],[ModifiedDate])
After executing the above query, if you run the script again, you will get the following result. The problematic rows have disappeared. A proper index has been created.
However, even without this kind of examination, it is possible to handle by checking the execution plan of SQL Server Management Studio during daily development. When the execution plan is displayed, if there are not enough indexes, they will be displayed as shown in the red frame below.
Right-click on the red frame to display the menu as shown below. Click "Missing Index Details..." from the menu.
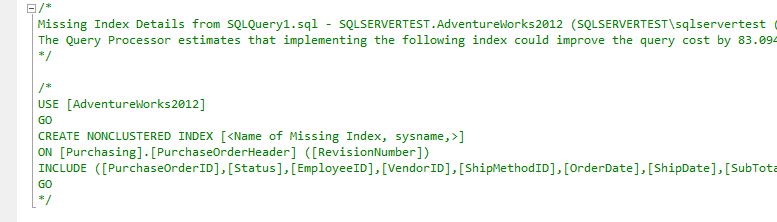
As shown in the figure below, CREATE INDEX statement will be generated.
The generated query is shown below. It also shows what percentage improvement, etc. (In this example, it seems to improve by 83.0941%.)
/* Missing Index Details from SQLQuery1.sql - SQLSERVERTEST.AdventureWorks2012 (SQLSERVERTEST\sqlservertest (53)) The Query Processor estimates that implementing the following index could improve the query cost by 83.0941%. */ /* USE [AdventureWorks2012] GO CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [<Name of Missing Index, sysname,>] ON [Purchasing].[PurchaseOrderHeader] ([RevisionNumber]) INCLUDE ([PurchaseOrderID],[Status],[EmployeeID],[VendorID],[ShipMethodID],[OrderDate],[ShipDate],[SubTotal],[TaxAmt],[Freight],[TotalDue],[ModifiedDate]) GO */
Be sure to check your queries in SQL Server Management Studio on a regular basis.
Ginger is a really useful website to check my grammar!!
www.getginger.jp